Digital skills among the representatives of cultural and creative industries in Kyrgyzstan: Interview with Erke Dzhumakmatova
In 2022, as part of the project of UNESCO Almaty, Erke Dzhumakmatova, a film producer, head of ‘OYMO Studio’ and researcher from Kyrgyzstan.
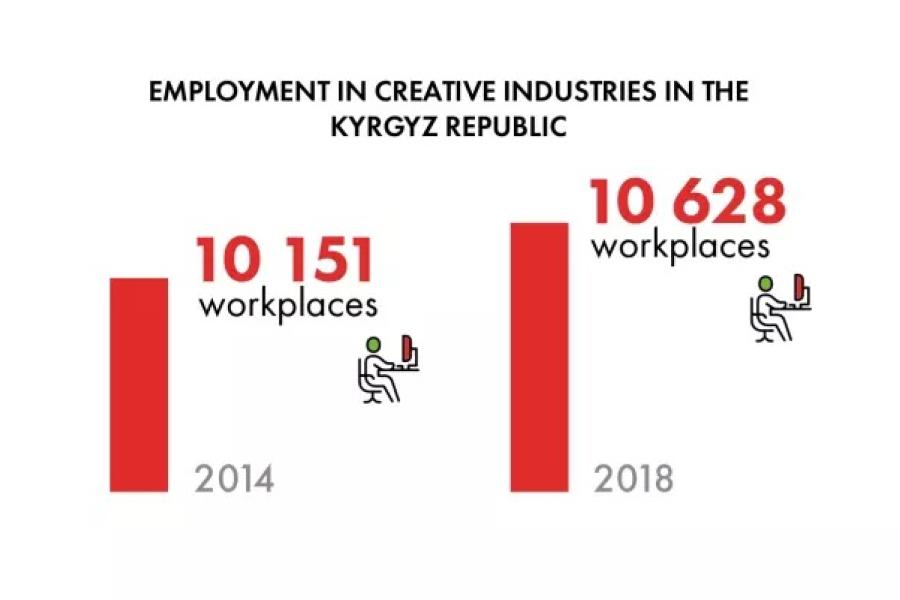
In 2022, as part of the project of UNESCO Almaty, Erke Dzhumakmatova, a film producer, head of ‘OYMO Studio’ and researcher from Kyrgyzstan, conducted a comprehensive study examining the state of affairs in her country’s creative industries, including film, music, and cultural events industries.
As part of the World Creativity and Innovation Day, celebrated on April 21, we asked Ms. Dzhumakmatova about the findings of the briefcase study and discussed the state of cultural and creative industries in Kyrgyzstan.
Q: Can you tell us about the study?
Erke Dzhumakmatova: This review was focused on the current state of digitalization in the creative industries in Kyrgyzstan, specifically in the areas of cinema, music, and cultural events. We all know that digitalization brought a significant change in the infrastructure and traditional approaches in these industries. But we also know there are still gaps in the development of digital skills among representatives of these areas.

Q: What are some of the challenges faced by representatives of the creative industries in Kyrgyzstan when it comes to digital skills?
Erke Dzhumakmatova: One of the main challenges is the limited understanding of the opportunities provided by modern technologies, which leads to a lack of use of social media, internet resources, mobile applications, and other digital tools. Additionally, the access to resources and digital technologies remains limited, and the creative class itself has a low count.
Q: What are some recommendations that emerged from your study to address these challenges?
Erke Dzhumakmatova: One of recommendations expressed as the result of the study is conducting outreach to leading representatives of these areas to introduce them to key digital concepts and tools. Additionally, creating accessible digital resources and educational platforms, developing infrastructure for working with multimedia across the country, and ensuring equal opportunities for promoting creative projects can also help develop digital skills in these areas. One of recommended initiatives is the creation of an educational platform and online courses on digital skills and competencies for the creative industries.
UNESCO
Q: Finally, how can society promote the development of digital skills in the creative industries?
Erke Dzhumakmatova: The principle of continuity of education, known as "life-long learning," is essential in promoting the development of digital skills in the creative industries. This principle emphasizes the importance of self-learning and continuing to develop throughout one's life, which contributes to the development of individual potential and the prosperity of society as a whole. Additionally, creating accessible digital resources and educational platforms can help make digital skills more widely available to people in the creative industries.

UNESCO
The United Nations designated 21 April as World Creativity and Innovation Day. On this day, we acknowledge and celebrate the role of creativity and innovation in all aspects of human development. We invite the world to embrace the idea that innovation is essential for harnessing the economic potential of nations. Innovation, creativity and mass entrepreneurship can provide new momentum towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). They can harness economic growth and job creation, while expanding opportunities for everyone, including women and youth. They can provide solutions to some of the most pressing problems such as poverty eradication and the elimination of hunger. Human creativity and innovation, at both the individual and group levels, have become the true wealth of nations in the twenty-first century.
UNESCO
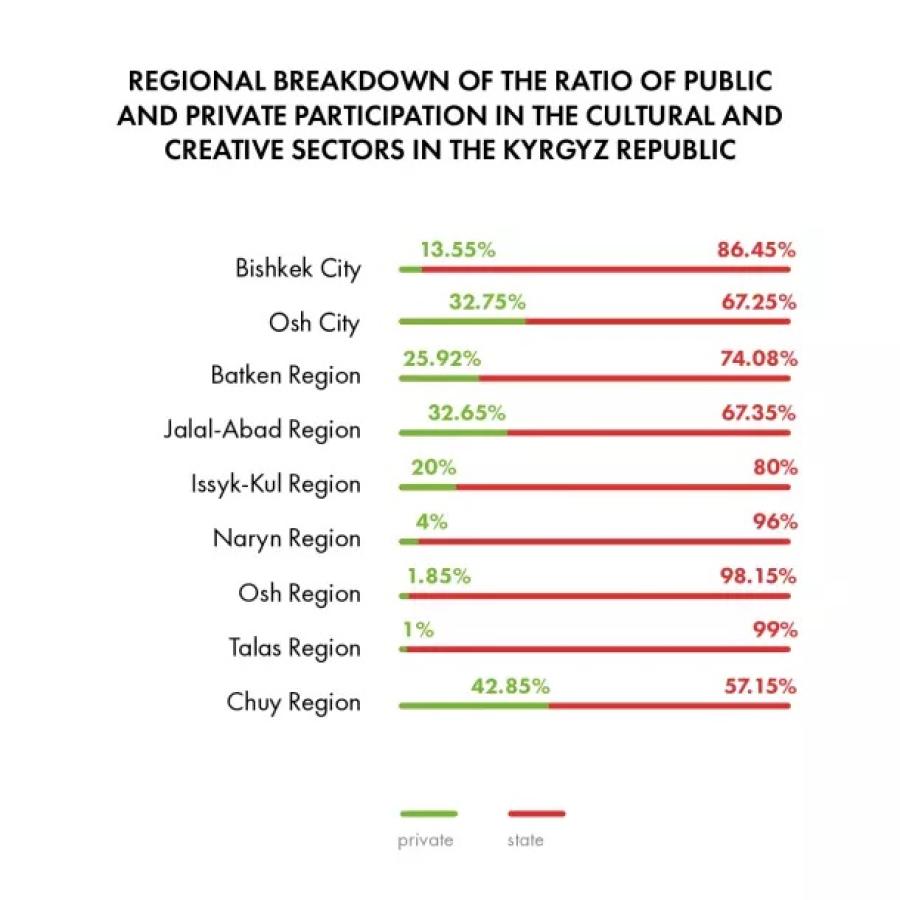
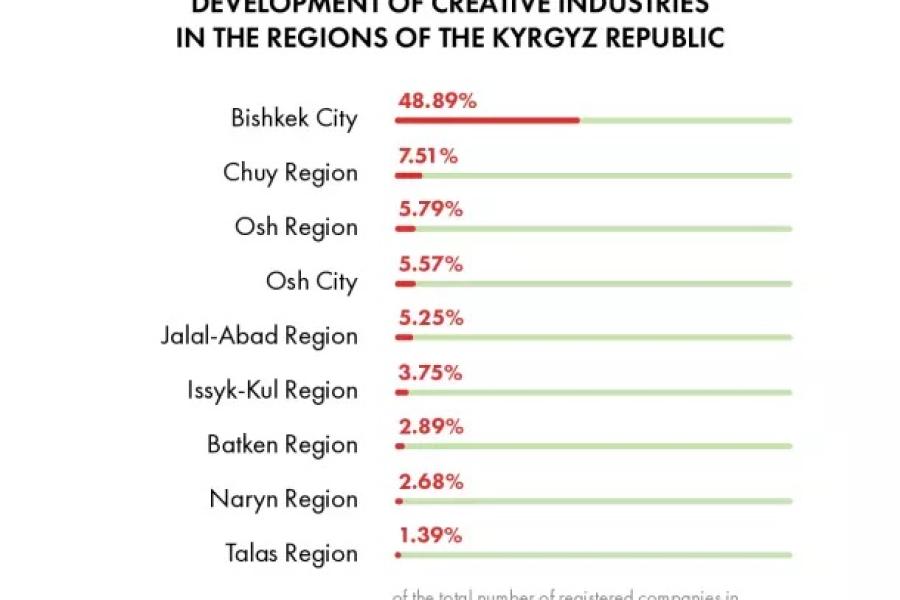
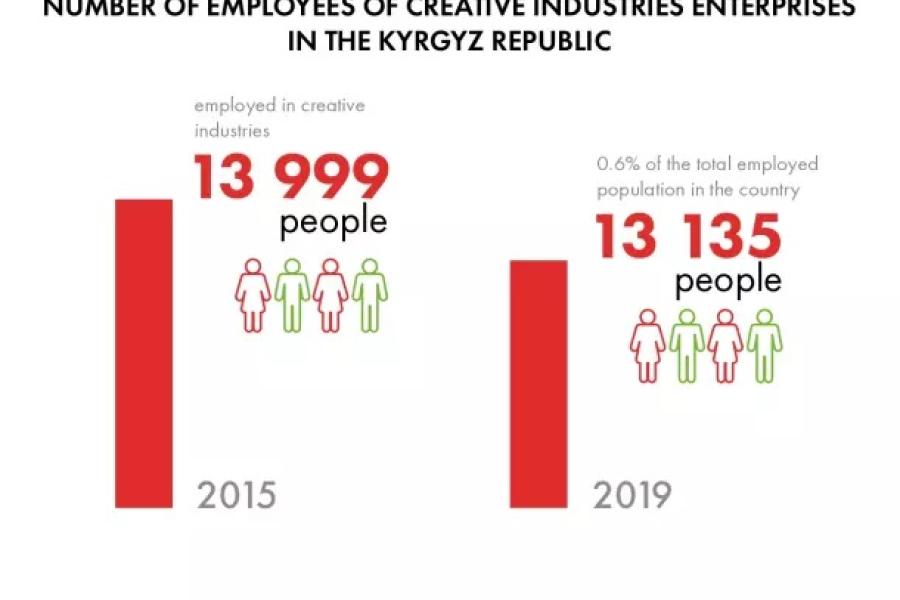
The “National Study of the Level of Development of Digital Skills in Music, Film and Organization of Cultural Events in the Republic of Kyrgyzstan” was conducted as part of UNESCO Almaty’s "Strengthening digital literacy skills and competencies and promoting gender equality in the cultural and creative sectors in Central Asia" project. The project is supported by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism of the Republic of Korea as part of the UNESCO Digital Creativity Lab.